Order fulfillment software revolutionizes the way businesses handle orders, ensuring seamless processing and delivery. Dive into the world of efficiency and optimization with this powerful tool at your disposal.
Definition of Order Fulfillment Software
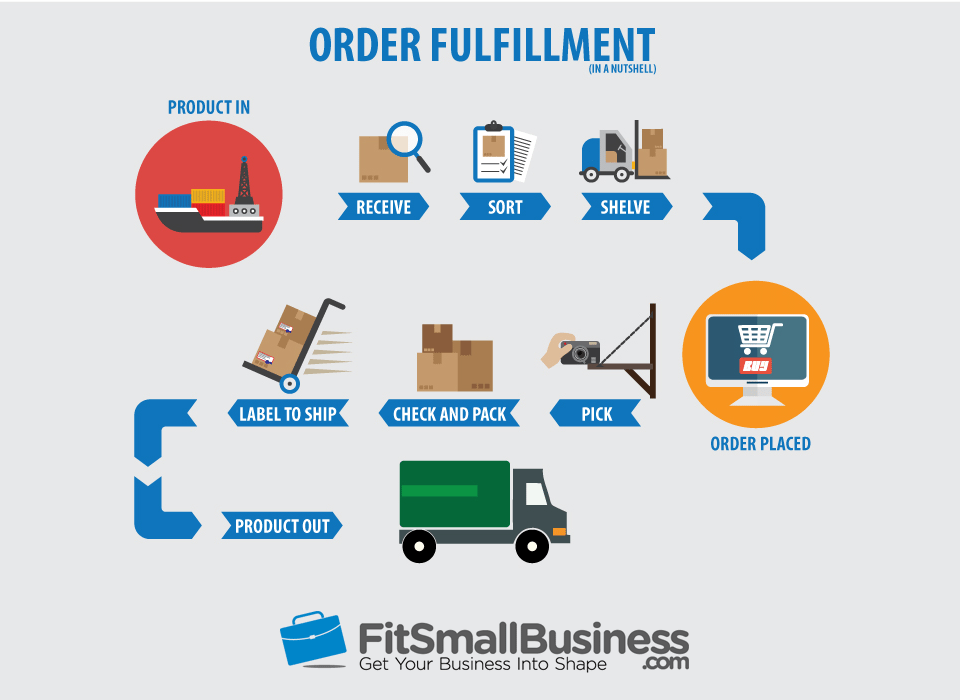
Order fulfillment software is a specialized tool used by businesses to manage and streamline the process of receiving, processing, and delivering customer orders. Its primary purpose is to ensure efficient order management, inventory tracking, and timely delivery to customers.
Key Features and Functionalities
- Order Processing: Automates the order processing workflow, from order placement to shipment.
- Inventory Management: Tracks inventory levels in real-time to prevent stockouts and overstocking.
- Shipping Integration: Integrates with shipping carriers to generate shipping labels and track deliveries.
- Order Tracking: Provides visibility into order status for both businesses and customers.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generates reports on order fulfillment metrics for performance analysis.
Benefits of Order Fulfillment Software
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlines order processing and reduces manual errors.
- Improved Accuracy: Ensures accurate order fulfillment and inventory management.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Enables faster order processing and delivery, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: Reduces labor costs and minimizes shipping errors through automation.
Types of Order Fulfillment Software
Order fulfillment software comes in various types tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries and business models. Let’s explore the different types available in the market.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems are designed to optimize and manage warehouse operations efficiently. They help in tracking inventory, picking, packing, and shipping orders. Examples of WMS include Fishbowl Warehouse, Snapfulfil, and NetSuite WMS.
Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
Transportation Management Systems focus on managing the transportation of goods from the warehouse to the customer. They help in route optimization, carrier selection, and tracking shipments. Examples of TMS include MercuryGate, Oracle TMS, and Descartes TMS.
Omni-channel Order Management Systems
Omni-channel Order Management Systems cater to businesses that sell through multiple channels such as online, brick-and-mortar stores, and marketplaces. They help in consolidating orders from different channels and managing inventory across all channels. Examples include Brightpearl, Orderbot, and ChannelAdvisor.
Scalability and Integration
Order fulfillment software is scalable, allowing businesses to adapt as they grow. Whether a business is small or large, the software can accommodate increasing order volumes and operational complexity. Additionally, order fulfillment software can integrate seamlessly with other systems like inventory management software, e-commerce platforms, and ERP systems. This integration streamlines operations, reduces errors, and improves overall efficiency.
Key Components and Modules
Order fulfillment software typically consists of several key components and modules that work together to streamline the order processing and delivery process for businesses. These components are essential in ensuring efficiency and accuracy in managing orders from placement to fulfillment. Let’s delve into the details of these crucial elements.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is a fundamental component of order fulfillment software as it allows businesses to track and manage their stock levels in real-time. By having accurate insights into inventory levels, businesses can prevent stockouts, reduce overstocking, and ensure timely order fulfillment. This module contributes to the overall efficiency of order processing by enabling businesses to fulfill orders promptly and accurately.
- Automated Stock Replenishment: Automatically reorder products when stock levels reach a specified threshold, minimizing the risk of stockouts.
- Batch Tracking: Track inventory by batch or lot numbers to ensure traceability and compliance with regulations.
- Multi-Warehouse Management: Manage inventory across multiple warehouses to optimize fulfillment and reduce shipping costs.
Order Management
The order management module facilitates the processing of orders from the moment they are placed until they are shipped to customers. It centralizes order information, automates order routing, and provides real-time order status updates. This component plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of order processing and delivery.
- Order Processing Automation: Automatically process orders based on predefined rules, reducing manual intervention and minimizing errors.
- Order Tracking: Provide customers with real-time tracking information to keep them informed about the status of their orders.
- Order Priority Settings: Assign priority levels to orders based on criteria such as order value, customer type, or shipping method.
Shipping and Logistics
The shipping and logistics module optimizes the shipping process by integrating with shipping carriers, generating shipping labels, and managing shipment tracking. It streamlines the fulfillment process by automating shipping tasks and providing visibility into the shipping status of orders.
- Carrier Integration: Integrate with major shipping carriers to access discounted rates, print shipping labels, and track shipments.
- Shipping Rules Configuration: Set up shipping rules based on factors like weight, destination, or shipping method to automate shipping calculations.
- Shipment Tracking: Provide customers with tracking information and notifications to enhance the post-purchase experience.
Customization Options
Many order fulfillment software solutions offer customization options to tailor the software to specific business needs. Businesses can customize workflows, reports, dashboards, and notifications to align with their unique requirements. This flexibility allows businesses to optimize their order fulfillment processes and improve overall operational efficiency.
Real-World Examples
For instance, an e-commerce retailer benefited from implementing batch tracking in their order fulfillment software, enabling them to trace products back to specific batches in case of quality issues. Another example is a subscription box service that utilized order priority settings to ensure that high-value subscribers received their boxes first, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Implementation and Integration
Implementing and integrating order fulfillment software within an organization is a crucial process that requires careful planning and execution. It involves setting up the software, configuring it to meet the specific needs of the business, and integrating it seamlessly with existing systems and workflows. Here are some best practices to consider:
Process of Implementing Order Fulfillment Software
- Define objectives and requirements: Clearly outline the goals and requirements for implementing the software to ensure a smooth transition.
- Select the right software: Choose a software solution that aligns with the unique needs of your business and offers the necessary features for efficient order fulfillment.
- Plan implementation timeline: Develop a detailed timeline for the implementation process, including key milestones and deadlines.
- Train employees: Provide comprehensive training to employees to ensure they are equipped with the knowledge and skills to effectively use the software.
- Monitor progress: Regularly monitor the implementation progress and address any issues or challenges that may arise during the process.
Integration with Existing Systems and Workflows
- Identify integration points: Determine the touchpoints between the order fulfillment software and existing systems to ensure seamless integration.
- Customize integration: Customize the integration process to accommodate the unique requirements of the business and optimize workflow efficiency.
- Test integration: Conduct rigorous testing to validate the integration and ensure that data flows smoothly between systems without any disruptions.
- Provide ongoing support: Offer continuous support to address any integration issues and optimize the performance of the software within the existing infrastructure.
Training and Onboarding Requirements
- Develop training materials: Create comprehensive training materials, including user guides and tutorials, to facilitate the onboarding process for employees.
- Offer hands-on training: Provide hands-on training sessions to allow employees to practice using the software in a simulated environment before going live.
- Assign dedicated support: Assign dedicated support staff to assist employees during the onboarding process and address any questions or concerns they may have.
Success Stories
- Company A streamlined their order fulfillment process by implementing order fulfillment software, resulting in a 20% increase in efficiency and a 15% reduction in order processing times.
- Company B integrated order fulfillment software with their existing inventory management system, leading to improved inventory accuracy and reduced stockouts by 30%.
Conclusive Thoughts
Embrace the future of order processing and delivery with order fulfillment software, where success stories and enhanced operations await.